The Entourage Effect and Cannabinoids: Understanding CB1 and CB2 Receptors and the Balance Between THC and CBD
Introduction
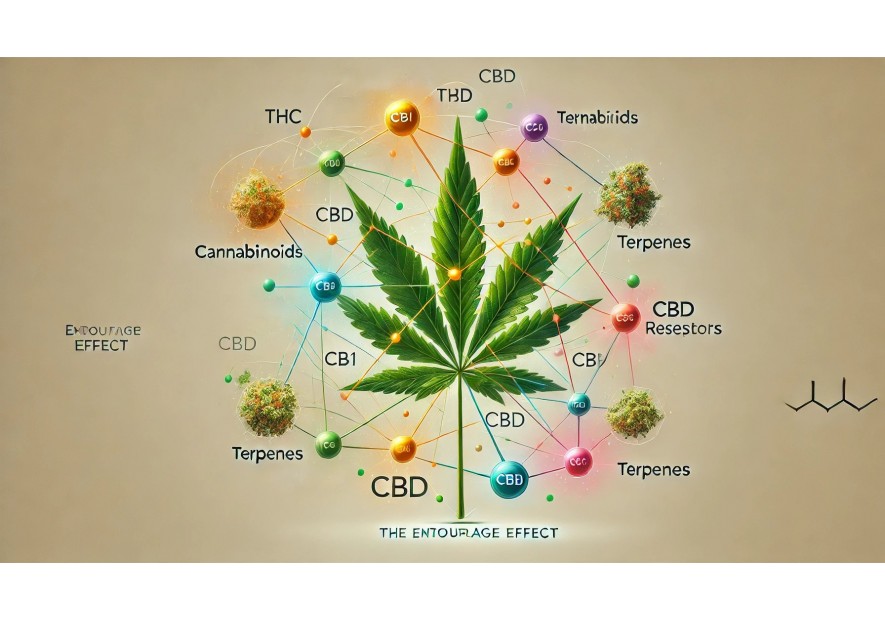
Cannabis is a multifaceted plant composed of various cannabinoids and terpenes that interact to create a complex range of effects on the human body. The entourage effect is a fascinating theory that suggests these compounds work in synergy to produce an overall experience richer than that offered by each component in isolation.
In this article, we will explore what the entourage effect is, how CB1 and CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system interact with cannabinoids, and why the balance between THC and CBD is crucial for a balanced cannabis consumption experience.
The Entourage Effect: A Natural Synergy
The entourage effect refers to how cannabinoids such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD (cannabidiol), CBN (cannabinol), and the terpenes present in cannabis work together to produce effects that are more complex and potent than if they were used separately.
For example, THC is well known for its psychoactive effects, but when consumed with CBD, its effects can be mitigated or modified. CBD has the ability to modulate the action of THC, which can reduce some of the undesirable effects such as anxiety or paranoia, while still allowing the consumer to benefit from THC's effects.
Terpenes, aromatic compounds found in cannabis, also play a crucial role in the entourage effect. They can influence how cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system and modulate the effects felt. For instance, myrcene, a terpene commonly found in cannabis, is known for its sedative properties and can enhance the relaxing effect of THC.
CB1 and CB2 Receptors: The Keys to Cannabinoid Interaction
- CB1 Receptors: These receptors are primarily located in the brain and central nervous system. THC binds directly to CB1 receptors, which is the origin of its psychoactive effects. By interacting with these receptors, THC can induce a "high" sensation, euphoria, but also, in some cases, unwanted side effects like anxiety.
- CB2 Receptors: These receptors are mainly found in the immune system and peripheral tissues. They are less involved in the psychoactive effects of cannabis and are more associated with the anti-inflammatory and therapeutic properties of cannabinoids. CBD and other non-psychoactive cannabinoids primarily interact with CB2 receptors, helping to modulate immune response and providing medical benefits without causing psychoactive effects.
The Balance Between THC and CBD: Finding the Right Dosage
One of the most important aspects of the entourage effect is the balance between THC and CBD. While THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects, CBD often plays a moderating role by attenuating some of the effects of THC.
For example, if you consume a cannabis strain rich in THC, you might experience intense euphoria, but also increased anxiety or paranoia. On the other hand, a strain with a higher ratio of CBD can offer a more balanced experience, where the effects of THC are present but less intense, thanks to CBD's moderating action.
Understanding this balance is essential, especially for those using cannabis for medical or recreational purposes. A good understanding of the entourage effect allows consumers to choose products that meet their specific needs, whether it's to relieve pain, reduce anxiety, or simply enjoy the psychoactive effects of cannabis in a more controlled way.
Conclusion
The entourage effect is a key component of the cannabis experience, explaining how different cannabinoids and terpenes interact to produce varied and often more potent effects. CB1 and CB2 receptors play a crucial role in how these compounds affect our bodies, while the balance between THC and CBD allows these effects to be modulated for a more pleasant and therapeutic experience.
By understanding these interactions, cannabis consumers can better control their experience and make the most of the many benefits this complex plant has to offer.






